·Dementia is a broad term that classifies a group of symptoms caused by disorders impairing the normal function of the brain. It is not one specific disease, but rather the collective effect of several.
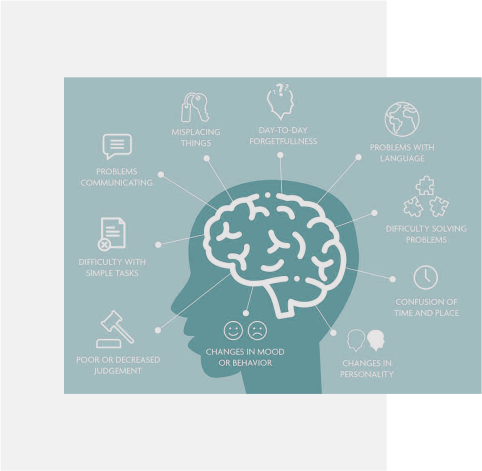
·Dementia affects memory, thinking, reasoning and behaviour. Brain function is impaired enough to interfere with the a persons ability to have a normal everyday life.
·No two cases of dementia are the same and it is not limited to those who are aged. As the saying goes “If you have met one person with Dementia, you have met one person with Dementia”
·An accurate medical diagnosis is essential when symptoms appear, not only for the patient’s own safety, but also because early diagnosis can improve the effectiveness of available treatments. Constant monitoring can avoid complications and relieve the stress on the resident and their family.
·Many patients lead very active and fulfilling lives for years after diagnosis.